Most common issues in stainless steel lost wax casting
2020-10-02Most Common issues in Stainless Steel Lost Wax Casting
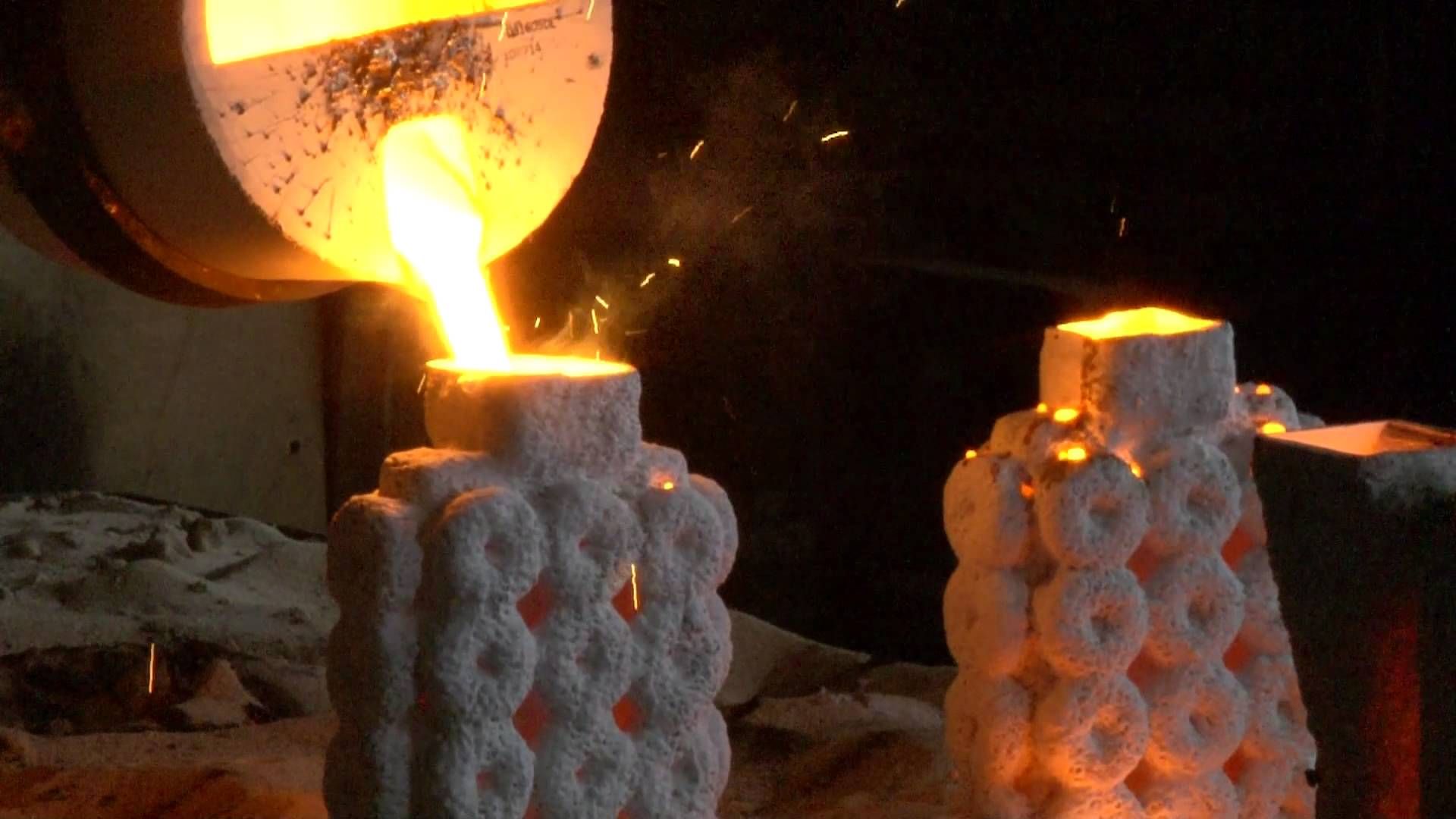
In the stainless steel lost wax casting process, two molds are used. The first is made of a metal. It can be easily worked in the inverted shape of the piece. This comes in two halves usually. Then, this mold is filled with wax to form the models. Hence, it is its final shape.
How stainless steel does lost wax casting model work?
These models are placed in a box. Moreover, these are filled with foundry sand. Later, an operator gives it heat until the wax melts. Similarly, he drips and another mold with the inverted shape of the piece.
This yes is filled with the molten metal. In addition, it gives rise to the piece. The advantages of this process are that several parts can be produced. Similarly, all parts come in a series with a high degree of detail and practically finished. Subsequently, the disadvantage is that the size of the pieces is limited.
What is casting?
The casting is the process where we mold different objects for multi purposes. In simple words, a metal comes in liquid state first. Later, it goes into a mold. Later, we can develop different shapes via stainless steel lost wax casting. So, we can use these molds for various industries.
In many cases, casting is the simplest and most economical process of producing a part.
The foundry can give rise to finished parts, already in their final shape, or not. In this case, they can undergo mechanical forming processes:
- dimensional adjustments
- welding or machining
But, in general, castings go through finishing processes such as:
- Grooving
- Machining
- and deburring
When necessary, the parts can also undergo heat treatment. It is to provide greater resistance since the stainless steel lost wax casting have less mechanical resistance.
How to transform the wax model into metal through lost wax casting?
Wax modeling is a jewelry technique to create shapes by sculpting the material. The result is a piece of wax. Moreover, it must be turned into metal by casting with lost wax.
Do we know this process?
The first step is the handmade production of the model in silver or wax. Therefore, we have two different starting points. It depends on the material in which the prototype was made.
To transform the wax piece into metal, the model is attached to a rod, also made of wax. It forms a “tree “also. As the process takes time and energy, usually the stainless steel lost wax casting completes with several parts in the same structure.
Moreover, these models can be different too. The final formation of the structure resembles a tree. This “tree” is placed inside a metal cylinder. And the calcium sulfate coating is poured into it.
Wax trees for the stainless steel lost wax casting process
After the coating hardens the cylinder gets heat to remove the wax. This expels, leaving empty spaces with the negative forms of future pieces.
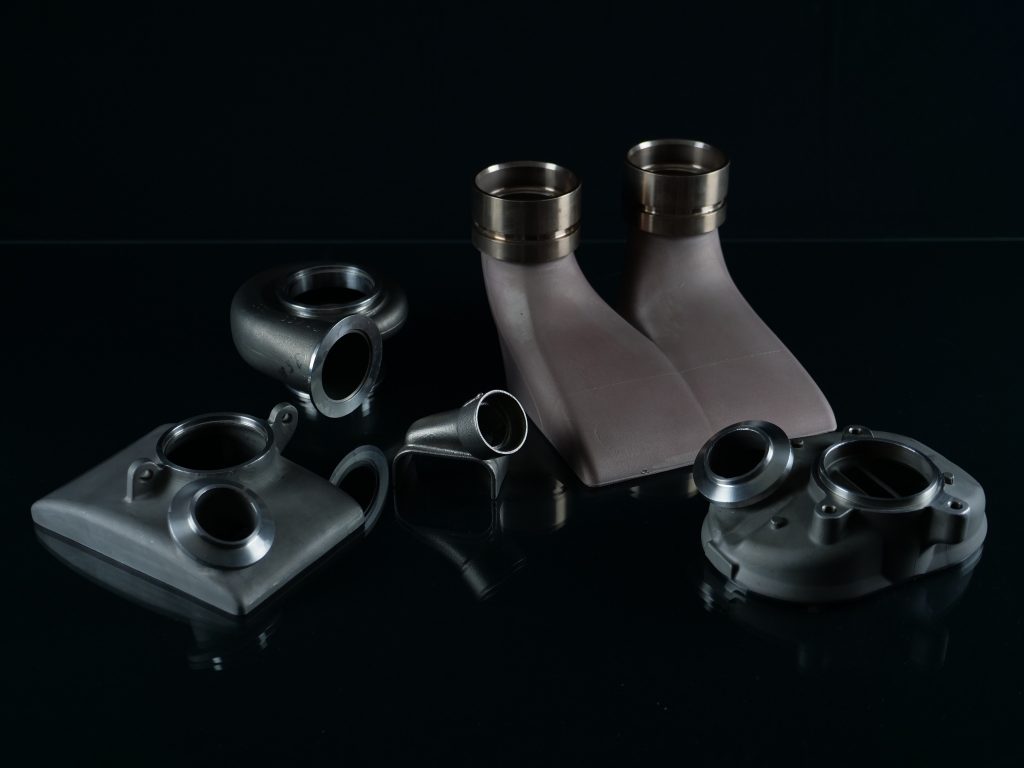

The metal is injected by centripetal force via stainless steel lost wax casting. It occupies the empty space left by the wax. After the metal has hardened, the coating is removed with cold water jets. The metal parts are removed from the “tree” with special pliers and go for assembly and finishing.
Serial reproduction
It is necessary to make copies of this piece or if the model is made of metal. The process begins by removing a rubber mold. This special rubber covers the pilot piece and is vulcanized. After heating, the rubber acquires a firm consistency.
Then, the rubber is opened, the pilot piece is removed. And, as a result, we have the negative shape of the pilot piece inside the rubber.
Models and rubber
By pressure, melted wax is injected into the mold. When the wax cools, we have a copy of the metal piece, only in wax. The wax piece is removed from the rubber mold. And it is ready to be used again. We can make as many wax copies as necessary.
The wax pieces are fixed on rods by stainless steel casting. It is also made of wax, forming a “tree”. And it follows the same process described above.
Stainless steel lost wax casting Problems
Some problems can occur during lost wax casting. The reasons for these defects to occur are diverse. Some of these causes are:
- When a hole occurs: poor quality wax or coating, overheated metal
- External balls occur: weak vacuum, lack of water in the coating mixture, badly beaten plaster
- When streaking occurs: excess water in the coating mixture.
What is the lost wax process?
Now let's talk about the theoretical part summarized for you to understand. In this type of production, a ceramic wrap is created around a prototype. It is usually made of wax or plastic. The prototype hardens to form the removable casting mold. It is called lost wax because during the process the liquid wax leaks. Moreover, it allows the initial piece to solidify.
Stainless steel lost wax casting process is repeated several times until you have the desired number of wax pieces. They are fixed in a structure that resembles a tree. It interconnects them all in a single entrance hole. This allows the temporary wax pieces to leave and the molten metal to enter.
Then, the tree is dipped in ceramic and touched up with sand. Similarly, it increases the resistance and hardening the piece. After that, this tree is heated again so that the piece has more structure and rigidity. This creates a hollow structure and allows for no thermal shock, which would cause the structure to break.
stainless steel lost wax casting conclusion
The transformations of metals depend mainly on stainless steel lost wax casting. It is evident that the casting is accompanied by several processes and stages. Here the appropriate choice of each step depends on the geometry of the part, the type of alloy to cast, the number of parts to be produced and the desired surface quality.
The main foundry processes are:
- Sand mold casting;
- Precision casting (lost wax);
- Casting of permanent gravity molds;
- Pressure casting;
- Centrifugal casting;




