Friction Stir Welding (FSW) Pros & Cons: (FSW vs Rotary Welding)
2020-11-23Friction welding: principle, advantages and applications
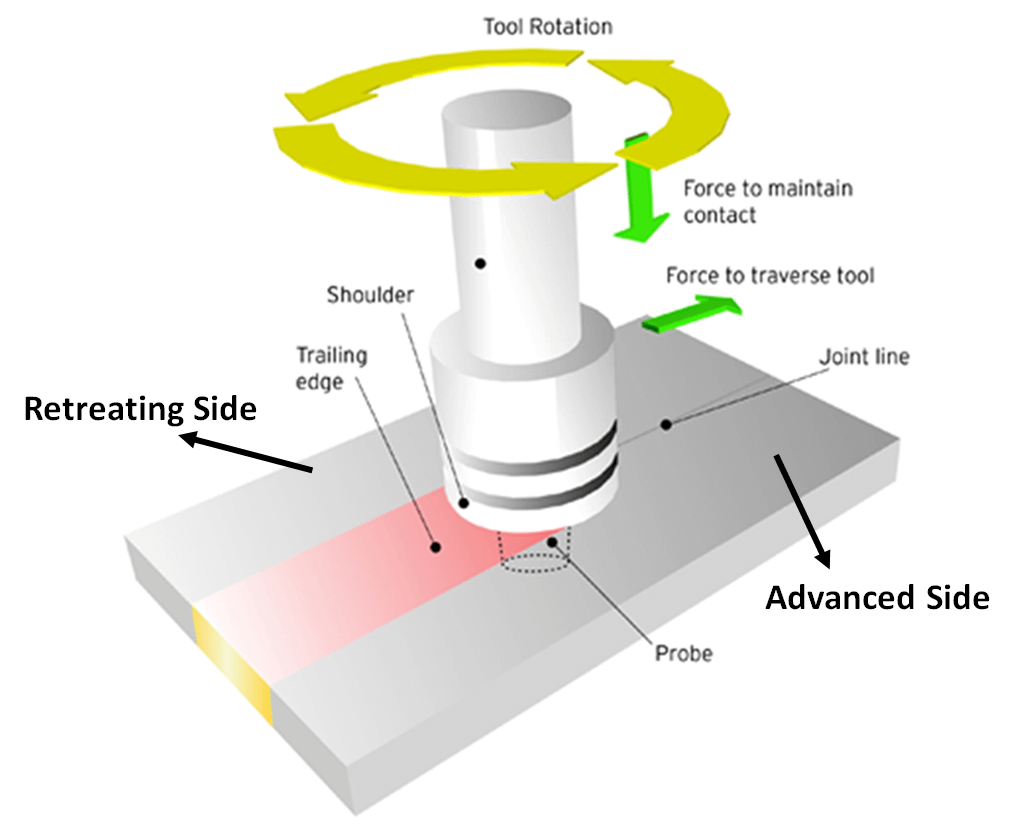
Friction Stir Welding (FSW) is a type of pressure welding. Here, the melt of the surfaces comes by converting the mechanical energy of the friction force of the parts into thermal energy.
Friction Stir Welding (FSW) - what is it?
Friction stir welding is a type of connection using pressure. It means that the parts to be welded will heat up as a result of friction against each other. One part remains stationary, while the other rotates, which allows the parts to connect with each other.
This method is quite new. And, perhaps, not all specialists or amateur welders had time to get acquainted with such welding technology. Therefore, we will read the principles of its operation, advantages, disadvantages, parameters, features and varieties of this method in more detail.
In this article we will look at:
- How Friction Stir Welding (FSW)works?
- What types of technology exist?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of friction welding?
Application and types of Friction Stir Welding (FSW)
Generally, friction welding is commonly applicable in the following operations:
- compounds of metals and alloys with a melting point of up to 1800 degrees
- welding flat parts of the same thickness at a turned angle
- longitudinal pipe welding
- making bolts
- Replacing soldering of small parts with machined surfaces.
Friction welding is suitable for joining contaminated parts, since it does not require their preliminary cleaning. Moreover, we remove the oxide film and grease at the beginning of mutual friction of the surfaces.
There are the following main types of friction welding:
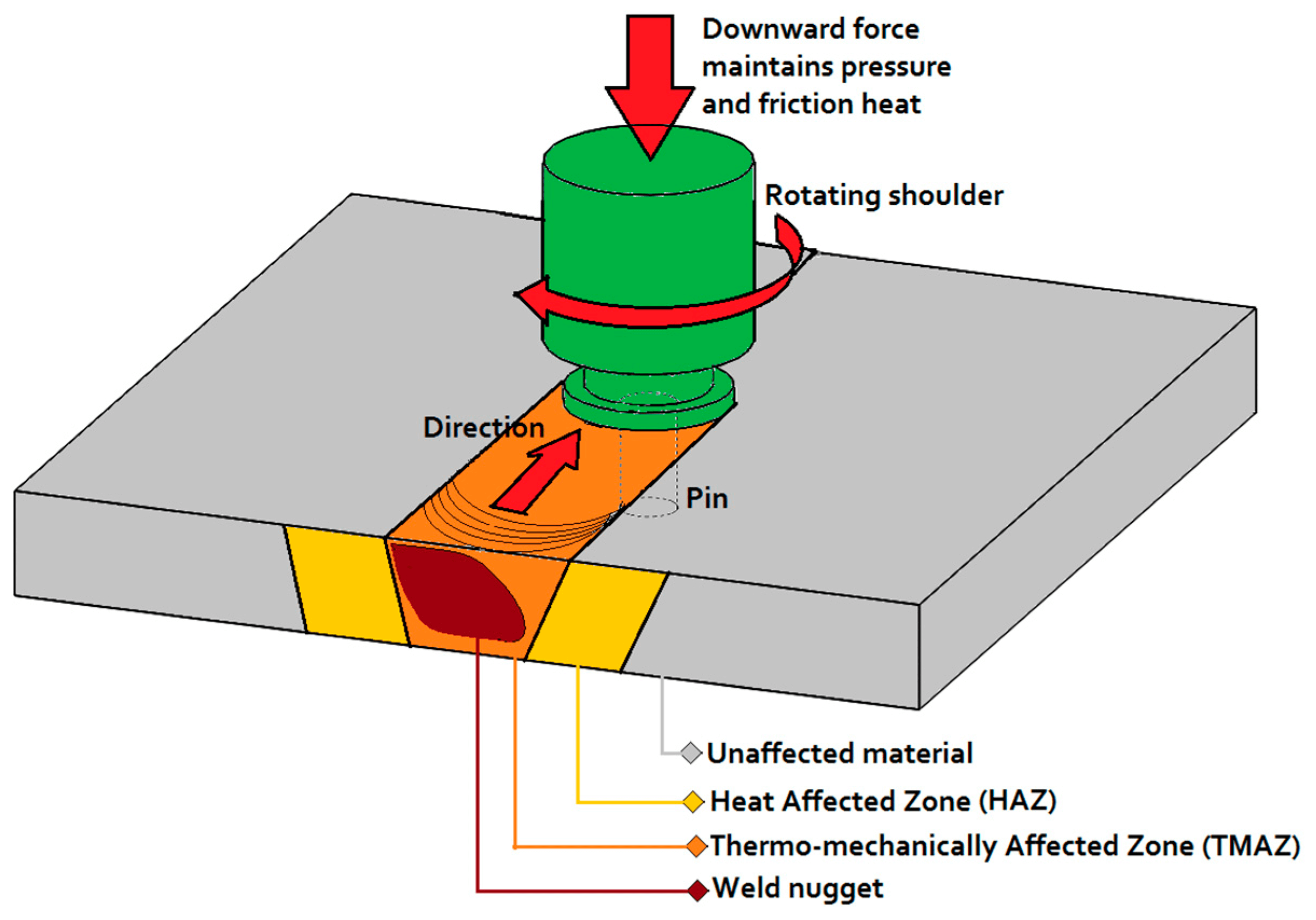
- oscillatory (linear)
- with stirring, with continuous drive
- radial
- orbital, inertial
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
The advantages of Friction Stir Welding (FSW) are:
- lower energy consumption compared to other types of welding
- Moreover, a small number of defects
- uniform structure of the weld
- the ability to accurately control the process
- Small amount of harmful emissions
- Hence, high metal utilization rate
- The ability to automate the process.

- Low requirements for surface cleanliness. There is no need to clean the surface of the parts to be welded. The side surfaces may also be uncleaned. Similarly, this significantly saves time spent on auxiliary operations.
- Possibility of welding various metals. The welding process allows welding both alloys and metals of the same name and dissimilar alloys. Furthermore, other welding methods are useless here. For example, it is possible to weld steel to aluminum, copper; aluminum with copper, titanium and so on.
- Hygienic process. The welding process compares favorably with the absence of ultraviolet radiation.
Disadvantages of the Friction Stir Welding (FSW):
- Friction Stir Welding (FSW) giveslimited applicability
- bulky equipment
- Limited connection surface.
Friction welding, principle and features:
Friction welding is a type of pressure welding in which heating goes out by friction caused by the rotation of the welded product.
Due to the emerging frictional forces at the points of contact, a very rapid heating and transition of the material into a plastic state occurs.
Thus, friction welding goes by a process in which mechanical energy supplied to one of the parts to be welded is converted into heat.
Friction welding is a process that converts the mechanical energy of the movement of one of the parts into heat energy. Rotation is the most common method for this. Similarly, either one of the parts or an insert between them can rotate. At the same time, the parts presses against each other by constant or increasing pressure. In this case, heating occurs directly at the junction of the parts.
How does Friction Stir Welding (FSW) work?
Friction Stir Welding (FSW) process is not so simple. After the completion of the welding process, upsetting occurs and the rotation stops quickly.
In the welding zone at the joints of the parts, the following processes take place: with an increase in the rotation frequency of the workpieces and the effect of compressive pressure, the contact surfaces rub against each other.
Similarly, fatty and contact films present on parts in their original state are destroyed. After which the boundary friction comes by dry friction. Hence, individual micro protrusions begin to contact each other and deform.
Juvenile areas form, where the bonds of surface atoms do not saturate. Moreover, metal bonds immediately appear between them. In addition, they immediately destroy due to the relative movement of the surfaces.
Principles of using friction stir welding for joints
This process means that one does during its rotation. Moreover, it will create thermal energy, as a result of which the materials combines with each other.
But not only one of the parts can rotate, but also a special tool for friction stir welding in the form of an insert. In addition, it also contributes to a high-quality connection of parts.
Friction welding: technology features
Friction welding is a subtype of pressure welding. The technology involves heating the parts to be welded using friction. For this, one of them moves (rotates), while welding with the other.
Application area of Friction Stir Welding (FSW)
Friction Stir Welding (FSW) is most widely applicable in mechanical engineering, primarily in tool production. It is also common in the assembly of internals of nuclear reactors. Friction bonding of aluminum and magnesium alloy workpieces is popular in:
- electrical engineering
- electronics and
- aerospace
The technology is also common in transport engineering. The radial method is famous in the production of equipment for the mining and processing industries.
Conclusion
More recently, Friction Stir Welding (FSW) has begun its journey in shipbuilding and food processing engineering.
We have covered such a process as friction welding. As you can see, this welding process is different from others, and has many advantages. However, it is quite specific and not suitable for all tasks. Nevertheless, in many cases its use is justified.
The technology demonstrates efficiency and a tendency to replace traditional welding methods in such areas as:
- to replace soldered and riveted joints;
- Replace contact electric welding;
- to restore products and complex tools;
- for welding workpieces to prepared surfaces




