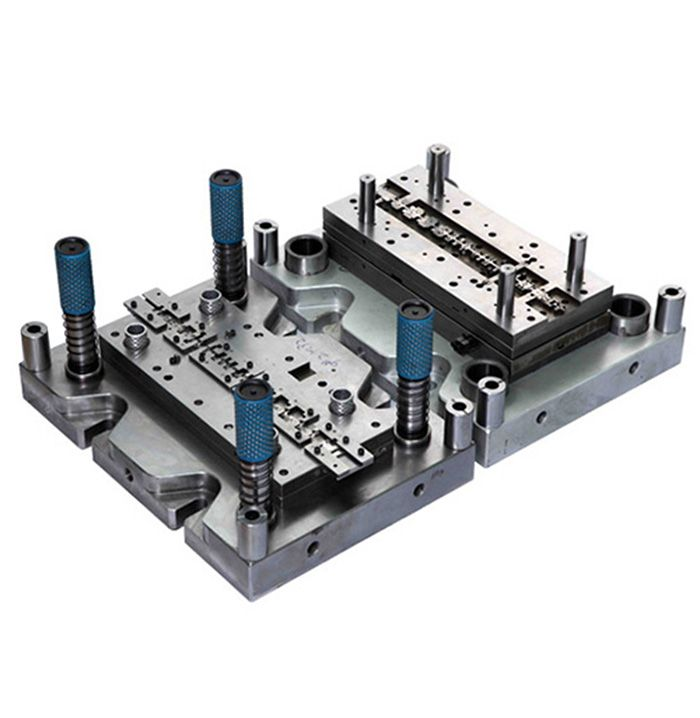
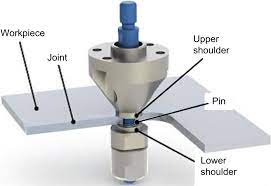
Casting bending die aluminum alloy is widely common for the manufacture of shaped castings. For this, pure aluminum or a product obtained as a result of secondary processing of raw materials can be common. The first option is common in the food and chemical industries, suitable for the production of electrical equipment. In general, aluminum accounts for about 20% of all cast alloys.

Features of bending die
When considering the features of this die, it is easy to note that pure aluminum is produced by specialized enterprises and cast into ingots. Secondary metallurgy uses scrap and other non-ferrous metal waste for casting. Thanks to the use of available raw materials, the cost of production also reduces.
If we turn to the statistics data, about half of world enterprises use aluminum bending die scrap. In Western countries, about 90% of all metallurgical plants use recyclable materials. This is due to the fact that recycling not only reduces the cost of production, but also ensures the ecological safety of the environment.
Application area
Due to the high consumer and physicochemical properties of the material, the field of use of aluminum casting is extensive and diverse. The material is inert to almost any environment and has increased corrosion resistance. At the same time, aluminum remains a light, but strong metal, which makes it possible to use it in various industries. Cast aluminum is suitable for the following purposes.
Manufacturing of body parts
For the bending die of such products, aluminum casting alloys are ideal. This is due to the fact that the cost of such products reduces. Considering that many body parts have a complex geometric shape, their production requires the use of milling equipment and appropriate tooling. Casting helps to achieve a similar result.
Parts for shipbuilding and aircraft construction
In this segment of the industry, aluminum is simply irreplaceable. The material is lightweight, so almost all aircraft parts come from it. In shipbuilding, aluminum has found application due to its corrosion resistance and resistance to sea water.
Production of parts with complex geometric shapes
Bending die represented by bodies of revolution and complex linear dimensions are resource-intensive in terms of machining. This requires sophisticated equipment, tooling, and highly qualified personnel. Foundry production is easier and cheaper.
Products for the electrical industry
Among other useful properties, aluminum has a high electrical conductivity. That is why the material is widely common in the manufacture of electrical wiring and other conductive elements. In addition to the above, aluminum has found application in engine building. It has good wear resistance.
The use of aluminum casting technologies makes it possible to obtain bending die with the highest possible precision. Moreover, the casting, carried out in compliance with all technological standards and requirements, provides a perfectly flat surface, which reduces the time and financial costs for subsequent processing.
Positive aspects
In conclusion, a number of positive aspects are easy to note. In particular, the cost of producing aluminum is low, especially when compared to other non-ferrous metals common in various industries. It is largely due to this feature that aluminum alloys are widely common for the needs of various enterprises.
In addition, the popularity of aluminum is due to the high performance properties of the material. It is a lightweight and durable bending die that can be common in any environment, including aggressive ones. That is why aluminum alloys are in demand in various industries.
What is pressing?
Pressing is one of the main methods of industrial processing of materials. The essence of the technological process is to increase the density of the feedstock and give the desired shape to the products. In addition, when performing such operations, the individual work pieces combine into a single product. Metal or composite materials can be common as raw materials.
How does metal pressing take place?
Metal pressing takes place by squeezing it out of a closed contour through a hole in the matrix. Composite materials are pressed in confined spaces by external compression. For this, molds are common, structurally consisting of a matrix and two punches
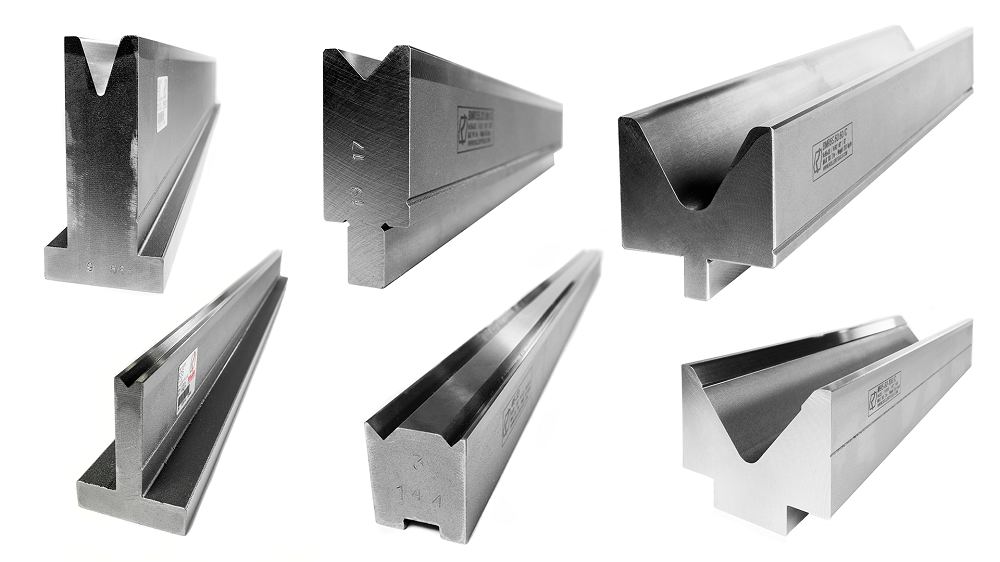
General Provisions
The manufacturing and engineering industries require a large number of high-precision tools as bending die. Moreover, such products should not only be accurate, but also easy to use, durable and as cheap as possible to manufacture. It is these tasks that determine the requirements for the materials common in tool making. The following types of steels are best for these purposes:
- Carbonaceous of ordinary quality
- Structural
- Instrumental
For which purpose tool steel is common?
Tool steel is common in the manufacture of measuring and cutting tools, individual assemblies of industrial molds and dies. It should be clarified that in the manufacture of cutting tools, such steel is not the only material. It also uses metal-ceramic plates and alloys, diamonds, etc.
Are other materials can be common with steel?
In the manufacture of bending die, it also allows to use other materials that are less durable than steel. The most common of these is gypsum. The dry mixture dilutes with water and stirred until a homogeneous mass obtains. The optimal consistency resembles thick sour cream.
The resulting mixture is poured into metal boxes, the lid and bottom of which are usually come in a removable version. For the manufacture of copier models, it allows to use wood, wax and other materials. In any case, the inner surfaces are carefully processed, all defects are eliminated.
Materials for making bending die depending on the pressing method
There are several ways to implement these technological processes. In the West, this technique was originally common to make parts of complex geometric shapes and precision forging metal ingots. The process is energy-consuming, but it provides the maximum production speed.
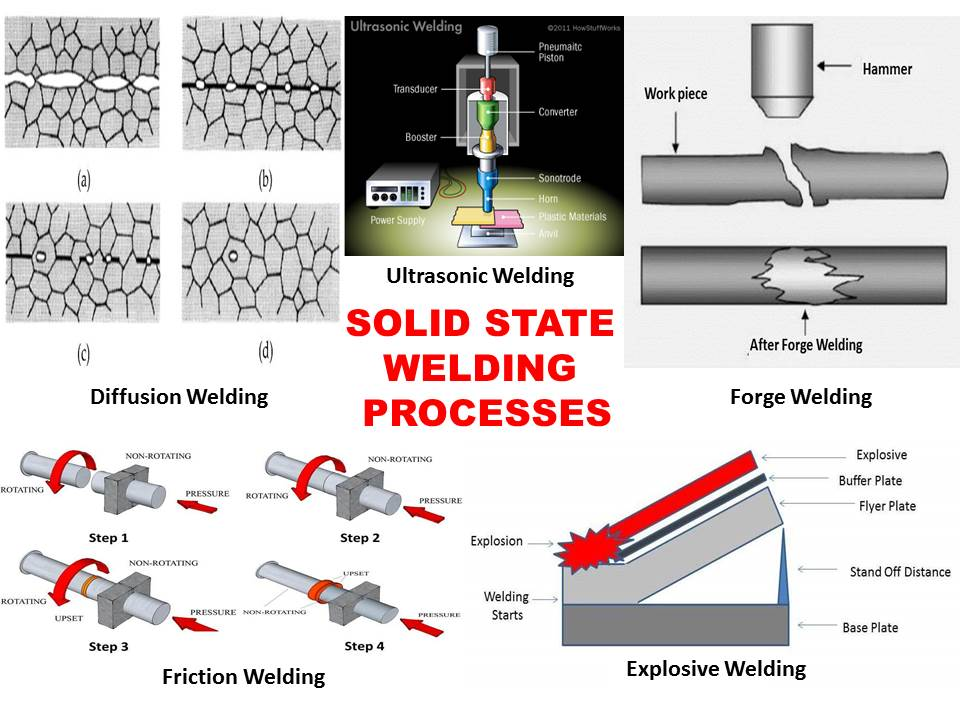
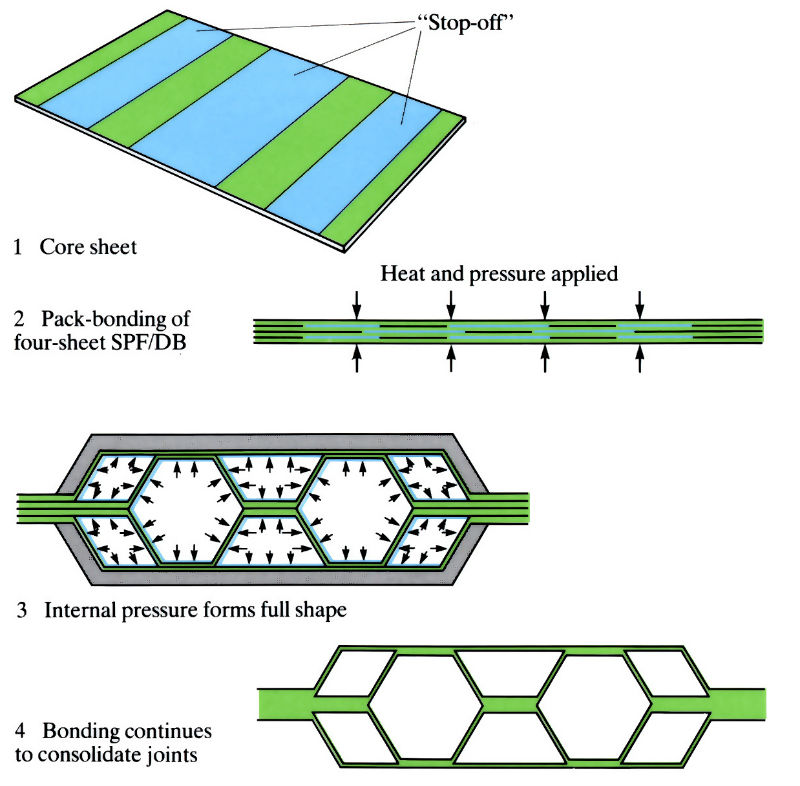
In fact, here we are talking about diffusion welding of raw materials heated to high temperatures using short-term external compression.
Production methodology
Considering the production methodology, bending die with heat-insulating coatings is common here. The main disadvantage of such molds is the high production cost. In addition, continuous operation at elevated temperatures leads to rapid destruction of working surfaces. The coatings have to change, which negatively affects the speed of the foundry.