What is metal stamping processing?
Metal stamping supplier provides the process of forming metal sheets in a desired shape using different manufacturing methods. The completion of a product usually involves many steps, from cutting and bending to surface treatment and assembly.
Often, fabrication techniques are easy to use to achieve similar end results, but the right choice should base on cost and need.
Metal stamping fabrication process
The journey from metal stamping to metal products begins with CAD, after which the models go through the necessary metal stamping fabrication processes. The most popular are:
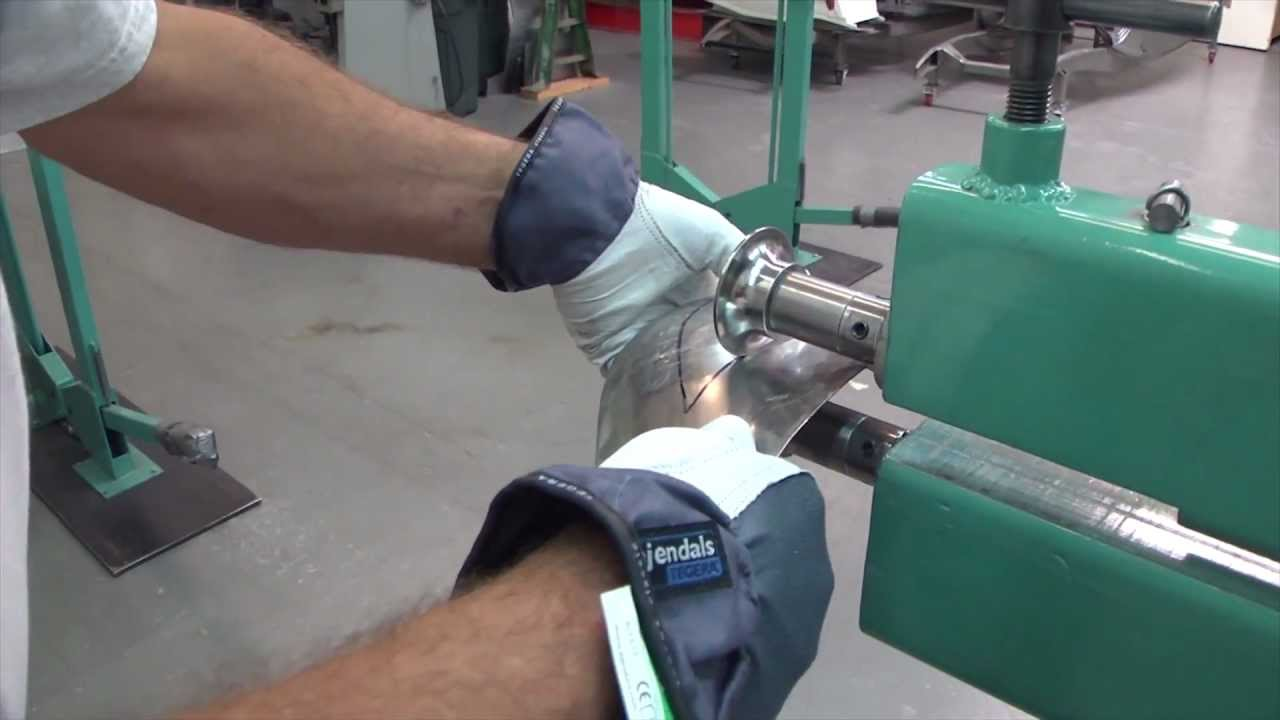
Laser cutting
Laser cutting is the preferred choice for Metal stamping supplier. A very fast and precise cutting method that guarantees good results. For thicker materials, plasma cutting is easy to use because of its quickness. But this advantage is only apparent with metals up to 10mm thick.
Cut
Cutting refers to a process of cutting metal stamping without melting. In essence, it's not too different from cutting with scissors. When cutting, the hammer presses the workpiece into the fixed die or blade, the gap causes the Metal stamping supplier cut. This is a great and effective method for cutting large metal sheets into other sizes (no complex engineering required).
Metal stamping Punching
Punching is another way to cut holes in sheet metal. A punch will deform the metal stamping into the desired shape or punch a hole in it. Punching is suitable for large-scale production but not cost-effective for small jobs. The reason is that punching requires separate tools for different shapes.
Curling
When it comes to actual engineering, there aren't many metal components that don't use bending techniques. Some bending shapes are complex and make manufacturing difficult.
Assemble
Assembly is the last or penultimate step when you want to build a product. If the assembly includes welding then cleaning and painting must accompany it. On the other hand, products that have been powder coated will be assembled together by other methods such as riveting, screwing...
Metal stamping supplier Powder Coating
Powder coating is a process in which an electrostatic powder is applied to an electrically charged metal component. This is the preferred surface treatment when there are no special requirements, such as acidic environments, which are common to the construction industry.
Advantages of sheet metal
- Flexible in design and use
- Production from prototype to bulk is possible
- There are many surface treatment options available: powder coating, painting, galvanizing, plating... allowing for a variety of looks and protection under different circumstances.
Application of sheet Metal stamping supplier
Metal stamping has many applications. It's not easy to find home appliances, construction... that don't use any Metal stamping supplier. However, different groups of metals have specific uses.
Cold rolled steel is used in home appliances, furniture, lockers, cabinets...Cold rolled steel is also used in warehouses and steel structures.
Do you know how the metal stamping process works?
Imagine producing your own detailed geometries using just a plate, a press and a few seconds. No welds, no chips, no mess and record time. This is Stamping!
Stamping is the manufacturing process for stamping metals, which through the pressing operation, plastically cuts or deforms metal sheets, generating a final product with an excellent finish. The process is very useful in industries with serial production and with large batches such as automotive and household appliances, for example.
Materials most used in Metal stamping
Of course, not all materials easy to use in Metal stamping supplier, you can only use those that are able to acquire the format of sheets or tapes, the main ones are:
- Steel
- Copper
- Aluminum
- Nickel
- Zinc
Metal stamping supplier high tooling cost
Although this type of manufacturing has a high tooling cost, making it impossible to apply for small batches, the advantages make it very attractive for several industries, because they can offer:
- high production
- Also, Low cost
- Moreover, great finish
- Furthermore, Greater strength of parts due to hardening of the material
- In addition, Production uniformity: Quality
Specific application of Metal stamping
Stamping has its strands and each one has its specific application, among them are: Cutting, Mechanical Conformation, Dip and Deep Metal stamping supplier. In all cases, the press exerts pressure on the sheet that, supported on a matrix, defines the profile of the part.
cut in stamping
The compression force exerted by the press is converted into shear force, cutting or perforating the material, thus producing profiles in flat pieces.
Some parts usually produced by this means of manufacturing are: IT components, cabinets, rulers, photo panels, washers or flat discs.
Mechanical Conformation of Metal stamping
In this category, the material does not necessarily need to undergo rupture, among the operations are the bending and bending, winding, ribbing and forming of tubes.
Examples of mechanical forming applications are the production of shallow parts such as car body components such as the hood and doors.

Drawing in the stamp
During this operation, the material undergoes a more intense conformation so that the material undergoes stretching, that is, its thickness is reduced so that it can be molded into the desired profile. It is important to remember that to be subjected to drawing, the material must meet certain specifications so that it does not break. An example of application are the sinks for kitchen sinks.
deep stamping
Following the same line of reasoning as in Shallow Stamping, in Metal stamping supplier the cup is deeper than half its diameter. An example of application of this stamping is in the production of pans.
Fine-Blanking or Fine Cut
Fine Cutting and Forming of Metal stamping supplier
it is the technology for the cost-effective production of precision-cut parts.
The fine cutting process offers state-of-the-art technology for the cost-effective production of parts with cutting precision and surfaces free from edges or burrs (cutting overflow). We can use them without any need for rework or second operation or process.
The development of projects
Of course, to produce the parts with the desired profiles, you will need the entire mechanical assembly and not just the die itself. Metal stamping supplier are composed of common elements (Base, head, guide columns and tenon) and specific elements, responsible for the profile of the part that will be produced ( dies and punches ).
Metal stamping supplier Dies and Punches
Dies and Punches are the fundamental elements of die tooling. In the matrix, the negative shape of the piece's profile is cut out and rigidly fix on a reinforce base, forming a solid set, whose material is of high quality and fine finish. Some characteristics that should consider in the design of cutting dies are:
- Exit angle to facilitate the flow of cut material;
- Also, Gap between punch and die that is responsible for cutting the desired piece;
- Moreover, they must not have sharp corners or very small rounding radii;
- Furthermore, they must not contain sudden variations in sections or blind holes.
Conclusion
In the fine cutting process, parts appear on a press with three active forces and on cutting tools with minimal clearance, at right angles with sharp surfaces that leave no burrs or edges and are extremely flat.






